笔者最近在完成抖音关注页面的仿写过程中了解到可以使用SDWebImage来进行头像加载的优化,当时只来得及了解其简单使用。现在有时间了,准备了解一下他的内部源码实现。
一、简介
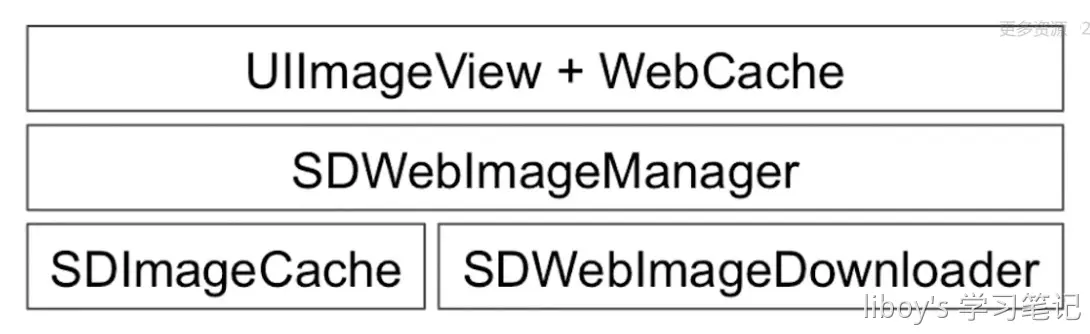
SDWebImage是iOS中提供图片加载的第三方库,可以给UIKit框架中的控件比如UIImageView和UIButton提供从网络上下载和缓存的图片。它的接口十分简洁,如果给UIImageView控件添加图片可以使用如下代码:
1
| [imageView sd_setImageWithURL:imageUrl placeholderImage:nil];
|
如果给UIButton 添加图片可以使用以下代码:
1
| [button sd_setImageWithURL:imageUrl forState:UIControlStateNormal placeholderImage:nil];
|
SDWebImage还提供了其他方法, 但是我们通过查看源码发现,最终都是调用气全能方法,全能方法还提供了占位图、可选项、加载进度和完成回调。
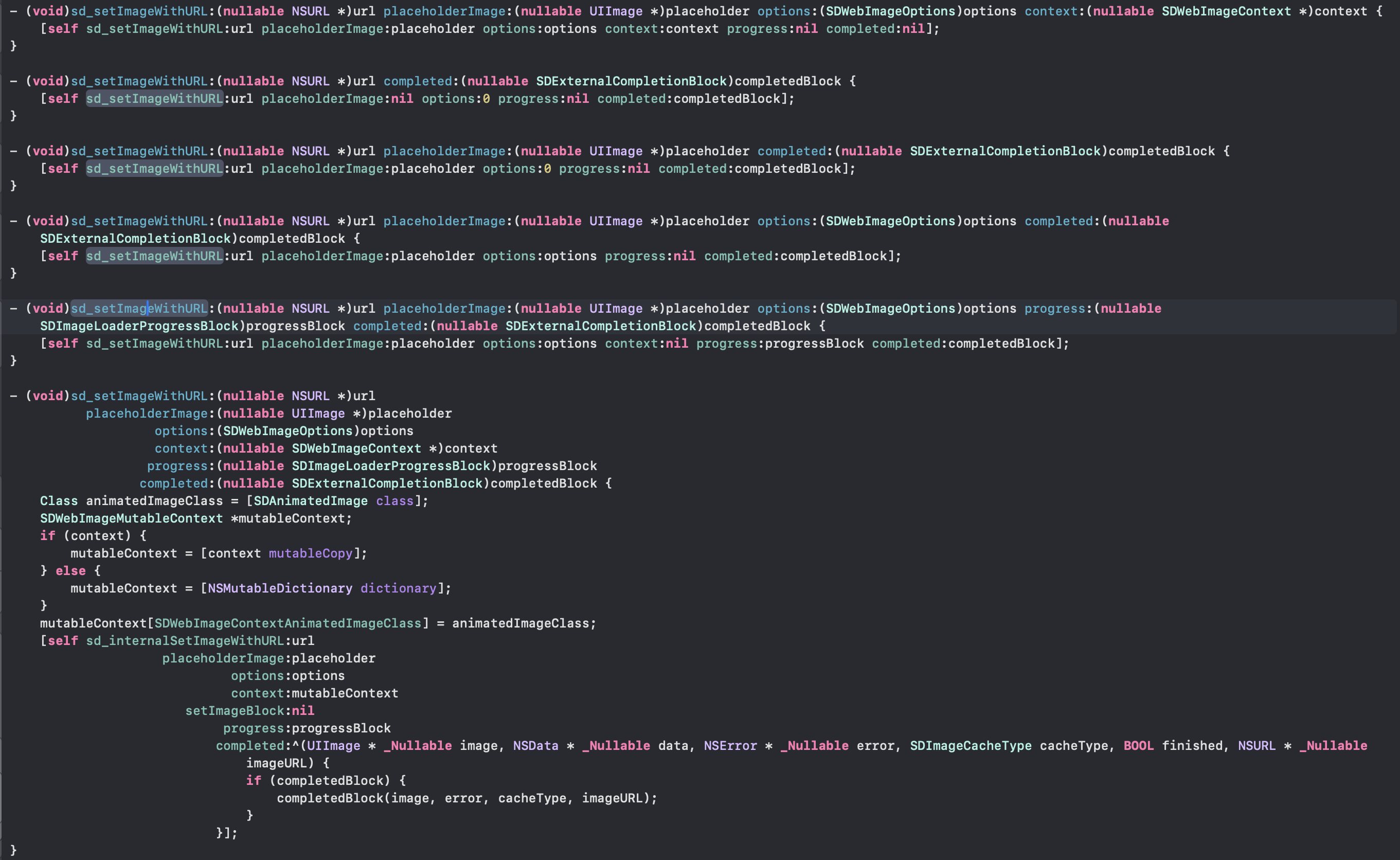
- 占位图像: 在网络图片加载过程中,ImageView会显示占位图像,给用户一个视觉上的暂时反馈。当网络图片加载完成后,ImageView中会显示加载完成的图片。
- 选项: 是一个枚举类型的值,用于设置加载图片的选项。其中包含了一些常用的选项,例如缓存策略、图片解码方式、加载优先级等。通过传递不同的选项,可以对图片加载的行为进行定制。
- 进度: 它们提供了对图片加载过程中的进度和结果的反馈。它们提供了对图片加载过程中的进度和结果的反馈。
- 完成回调: 是一个块对象,用于在图片加载完成后执行相应的操作。
SDWebImage有下面一些常见的功能:
- 通过异步方式加载图片
- 可以自动缓存到内存和磁盘中,并且可以自动清理过期的缓存
- 支持多种的图片格式包括jpg、jepg、png等,同时还支持多种动图格式包括GIF、APNG等
- 同一图片的URL不会重复下载
- 在子线程中进行操作,确保不会阻塞主线程
二、SDWebImage调用流程
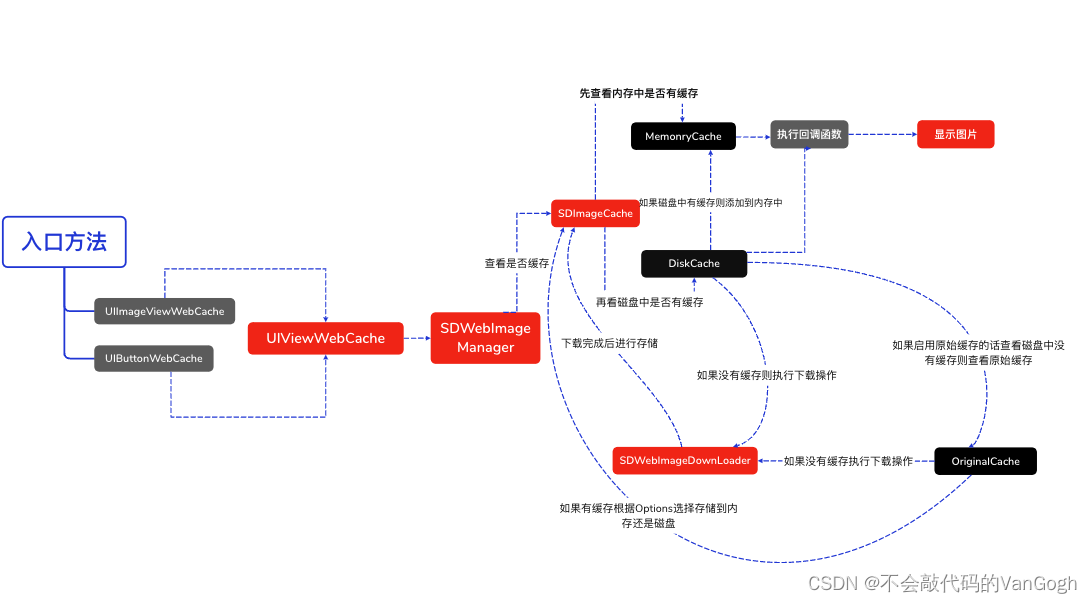
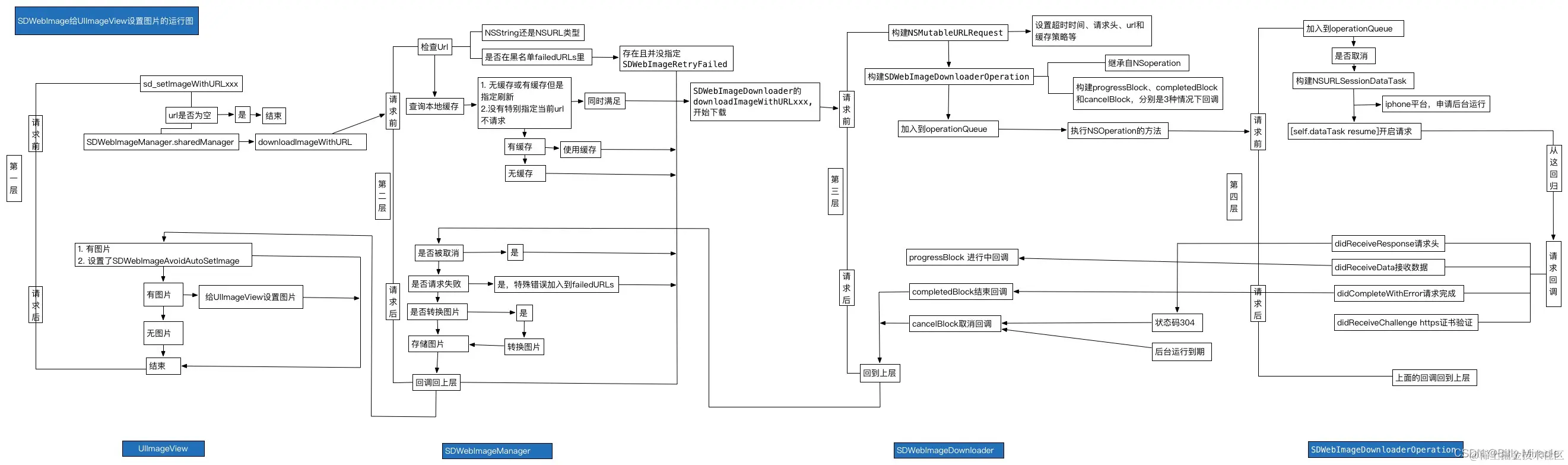
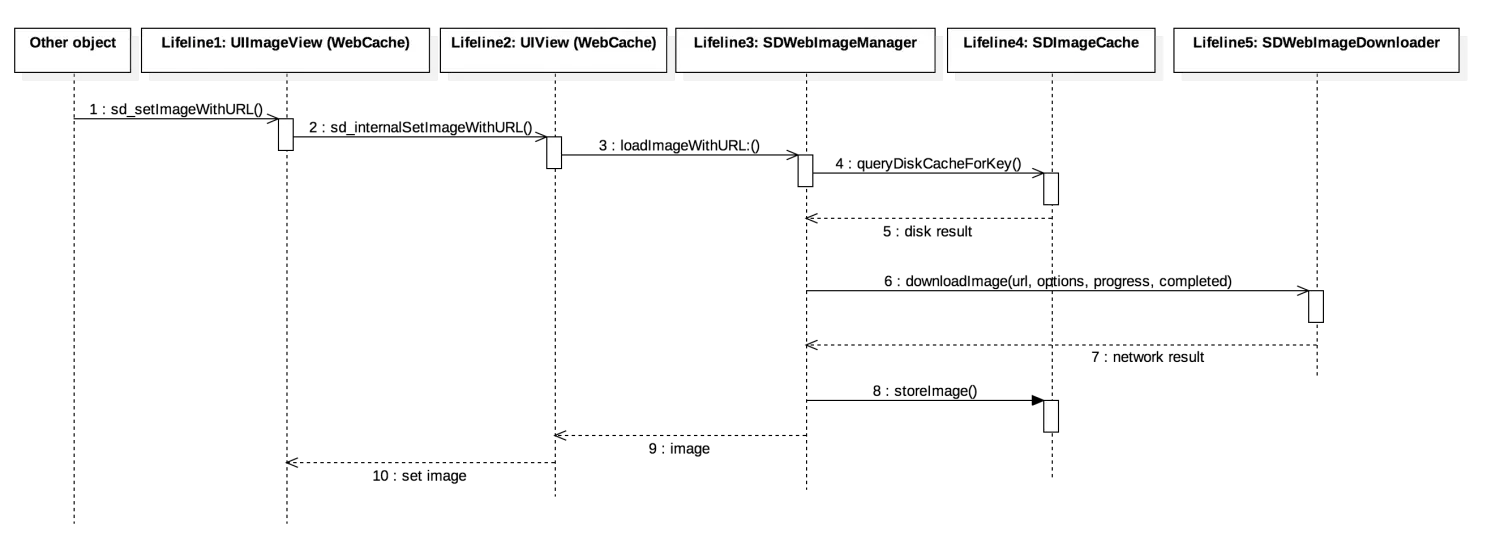
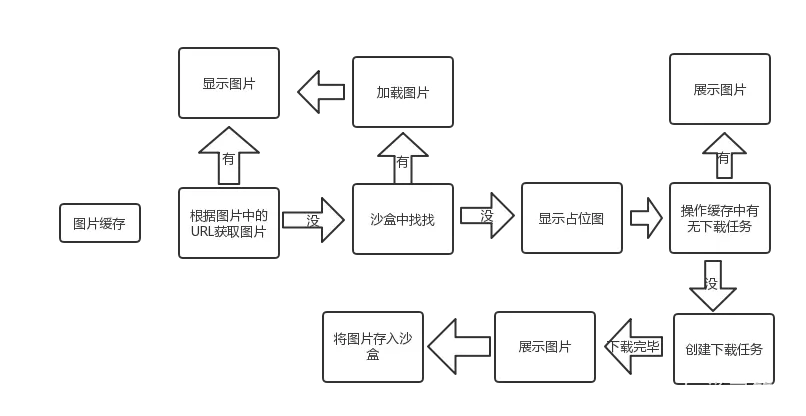
当使用[imageView sd_setImageWithURL:imageUrl placeholderImage:nil];方法时,会执行UIImageView+WebCache类中的相应方法,当使用[button sd_setImageWithURL:imageUrl forState:UIControlStateNormal placeholderImage:nil];方法时会执行UIBUtton+WebCache类中的相应方法,但是最后都会调用UIView+WebCache类中的- (nullable id<SDWebImageOperation>)sd_internalSetImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url placeholderImage:(nullable UIImage *)placeholder options:(SDWebImageOptions)options context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context setImageBlock:(nullable SDSetImageBlock)setImageBlock progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {};方法。接着根据URL,通过SDWebImageManager的loadImageWithURL:options:context:progress:completed:方法加载图片,接着通过sd_setImageLoadOperation方法将operation加入到SDOperationsDictionary中。然后调用queryCacheOperationForKey方法进行查询图片缓存,通过查询内存和磁盘中是否有缓存,如果有则通过SDImageCacheDelegate回调imageCache:didFindImage:forkey:userInfo到SDWebImageManager,然后其回调webImageManager:didFinishWithImage:到UIImageView + WebCache前短展示页面。
根据URLKye在硬盘缓存目录尝试读取图片文件,这一步在NSOperation操作,回主线程结果回调notifyDelegate:
如果从硬盘读取到了图片,将图片添加到内存缓存中(如果空闲内存过小,会先清空内存缓存)。SDImageCacheDelegate回调 imageCache:didFindImage:forKey:userInfo:进而回调展示图片。
如果从硬盘缓存目录读取不到图片,说明所有缓存都不存在该图片,需要下载图片,回调 imageCache:didNotFindImageForKey:userInfo:。
共享或重新生成一个下载器 SDWebImageDownloader 开始下载图片。
图片下载由 NSURLConnection (3.8.0 之后使用了 NSURLSession),实现相关 delegate 来判断图片下载中、下载完成和下载失败。
connection:didReceiveData:中利用 ImageIO 做了按图片下载进度加载效果。
connectionDidFinishLoading: 数据下载完成后交给 SDWebImageDecoder做图片解码处理。图片解码处理在一个 NSOperationQueue 完成,不会拖慢主线程 UI。如果有需要对下载的图片进行二次处理,最好也在这里完成,效率会好很多。
在主线程 notifyDelegateOnMainThreadWithInfo:宣告解码完成,imageDecoder:didFinishDecodingImage:userInfo:回调给 SDWebImageDownloader。
imageDownloader:didFinishWithImage: 回调给 SDWebImageManager告知图片下载完成。
通知所有的downloadDelegates下载完成,回调给需要的地方展示图片。
将图片保存到SDImageCache中,内存缓存和硬盘缓存同时保存。写文件到硬盘也在以单独 NSInvocationOperation 完成,避免拖慢主线程。
SDImageCache 在初始化的时候会注册一些消息通知,在内存警告或退到后台的时候清理内存图片缓存,应用结束的时候清理过期图片。
SDWebImagePrefetcher可以预先下载图片,方便后续使用。
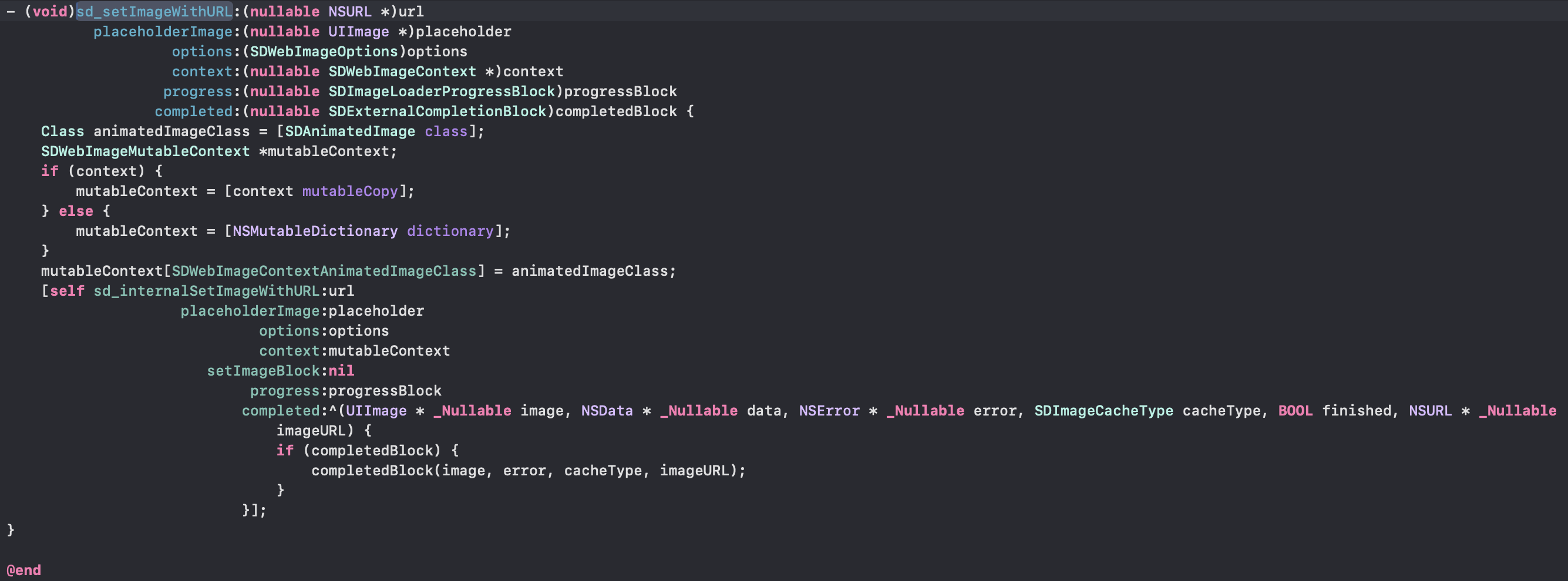
通过进一步探索,我们可以找到他的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
| - (nullable id<SDWebImageOperation>)sd_internalSetImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
placeholderImage:(nullable UIImage *)placeholder
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
setImageBlock:(nullable SDSetImageBlock)setImageBlock
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
if ([url isKindOfClass:NSString.class]) {
url = [NSURL URLWithString:(NSString *)url];
}
if (![url isKindOfClass:NSURL.class]) {
url = nil;
}
if (context) {
context = [context copy];
} else {
context = [NSDictionary dictionary];
}
NSString *validOperationKey = context[SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey];
if (!validOperationKey) {
validOperationKey = NSStringFromClass([self class]);
SDWebImageMutableContext *mutableContext = [context mutableCopy];
mutableContext[SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey] = validOperationKey;
context = [mutableContext copy];
}
self.sd_latestOperationKey = validOperationKey;
if (!(SD_OPTIONS_CONTAINS(options, SDWebImageAvoidAutoCancelImage))) {
[self sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey:validOperationKey];
}
SDWebImageLoadState *loadState = [self sd_imageLoadStateForKey:validOperationKey];
if (!loadState) {
loadState = [SDWebImageLoadState new];
}
loadState.url = url;
[self sd_setImageLoadState:loadState forKey:validOperationKey];
SDWebImageManager *manager = context[SDWebImageContextCustomManager];
if (!manager) {
manager = [SDWebImageManager sharedManager];
} else {
SDWebImageMutableContext *mutableContext = [context mutableCopy];
mutableContext[SDWebImageContextCustomManager] = nil;
context = [mutableContext copy];
}
SDCallbackQueue *queue = context[SDWebImageContextCallbackQueue];
BOOL shouldUseWeakCache = NO;
if ([manager.imageCache isKindOfClass:SDImageCache.class]) {
shouldUseWeakCache = ((SDImageCache *)manager.imageCache).config.shouldUseWeakMemoryCache;
}
if (!(options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder)) {
if (shouldUseWeakCache) {
NSString *key = [manager cacheKeyForURL:url context:context];
[((SDImageCache *)manager.imageCache) imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
}
[(queue ?: SDCallbackQueue.mainQueue) async:^{
[self sd_setImage:placeholder imageData:nil basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock cacheType:SDImageCacheTypeNone imageURL:url];
}];
}
id <SDWebImageOperation> operation = nil;
if (url) {
NSProgress *imageProgress = loadState.progress;
if (imageProgress) {
imageProgress.totalUnitCount = 0;
imageProgress.completedUnitCount = 0;
}
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
[self sd_startImageIndicatorWithQueue:queue];
id<SDWebImageIndicator> imageIndicator = self.sd_imageIndicator;
#endif
SDImageLoaderProgressBlock combinedProgressBlock = ^(NSInteger receivedSize, NSInteger expectedSize, NSURL * _Nullable targetURL) {
if (imageProgress) {
imageProgress.totalUnitCount = expectedSize;
imageProgress.completedUnitCount = receivedSize;
}
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
if ([imageIndicator respondsToSelector:@selector(updateIndicatorProgress:)]) {
double progress = 0;
if (expectedSize != 0) {
progress = (double)receivedSize / expectedSize;
}
progress = MAX(MIN(progress, 1), 0);
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[imageIndicator updateIndicatorProgress:progress];
});
}
#endif
if (progressBlock) {
progressBlock(receivedSize, expectedSize, targetURL);
}
};
@weakify(self);
operation = [manager loadImageWithURL:url options:options context:context progress:combinedProgressBlock completed:^(UIImage *image, NSData *data, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL *imageURL) {
@strongify(self);
if (!self) { return; }
if (imageProgress && finished && !error && imageProgress.totalUnitCount == 0 && imageProgress.completedUnitCount == 0) {
imageProgress.totalUnitCount = SDWebImageProgressUnitCountUnknown;
imageProgress.completedUnitCount = SDWebImageProgressUnitCountUnknown;
}
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
if (finished) {
[self sd_stopImageIndicatorWithQueue:queue];
}
#endif
BOOL shouldCallCompletedBlock = finished || (options & SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage);
BOOL shouldNotSetImage = ((image && (options & SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage)) ||
(!image && !(options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder)));
SDWebImageNoParamsBlock callCompletedBlockClosure = ^{
if (!self) { return; }
if (!shouldNotSetImage) {
[self sd_setNeedsLayout];
}
if (completedBlock && shouldCallCompletedBlock) {
completedBlock(image, data, error, cacheType, finished, url);
}
};
if (shouldNotSetImage) {
[(queue ?: SDCallbackQueue.mainQueue) async:callCompletedBlockClosure];
return;
}
UIImage *targetImage = nil;
NSData *targetData = nil;
if (image) {
targetImage = image;
targetData = data;
} else if (options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder) {
targetImage = placeholder;
targetData = nil;
}
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
SDWebImageTransition *transition = nil;
BOOL shouldUseTransition = NO;
if (options & SDWebImageForceTransition) {
shouldUseTransition = YES;
} else if (cacheType == SDImageCacheTypeNone) {
shouldUseTransition = YES;
} else {
if (cacheType == SDImageCacheTypeMemory) {
shouldUseTransition = NO;
} else if (cacheType == SDImageCacheTypeDisk) {
if (options & SDWebImageQueryMemoryDataSync || options & SDWebImageQueryDiskDataSync) {
shouldUseTransition = NO;
} else {
shouldUseTransition = YES;
}
} else {
shouldUseTransition = NO;
}
}
if (finished && shouldUseTransition) {
transition = self.sd_imageTransition;
}
#endif
[(queue ?: SDCallbackQueue.mainQueue) async:^{
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
[self sd_setImage:targetImage imageData:targetData options:options basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock transition:transition cacheType:cacheType imageURL:imageURL callback:callCompletedBlockClosure];
#else
[self sd_setImage:targetImage imageData:targetData basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock cacheType:cacheType imageURL:imageURL];
callCompletedBlockClosure();
#endif
}];
}];
[self sd_setImageLoadOperation:operation forKey:validOperationKey];
} else {
#if SD_UIKIT || SD_MAC
[self sd_stopImageIndicatorWithQueue:queue];
#endif
if (completedBlock) {
[(queue ?: SDCallbackQueue.mainQueue) async:^{
NSError *error = [NSError errorWithDomain:SDWebImageErrorDomain code:SDWebImageErrorInvalidURL userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey : @"Image url is nil"}];
completedBlock(nil, nil, error, SDImageCacheTypeNone, YES, url);
}];
}
}
return operation;
}
|
这个方法简要流程:
- 讲
SDWebImageContext 复制并转换为immutable,获取其中的validOperationkey值作为校验值id,默认值为当前view的类名
- 执行 sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey 取消上一次任务,保证没有当前正在进行的异步下载操作, 不会与即将进行的操作发生冲突;
- 设置占位图;
- 初始化 SDWebImageManager 、SDImageLoaderProgressBlock , 重置 NSProgress、SDWebImageIndicator;
- 开启下载loadImageWithURL: 并将返回的 SDWebImageOperation 存入 sd_operationDictionary,key 为 validOperationKey;
- 取到图片后,调用 sd_setImage: 同时为新的 image 添加 Transition 过渡动画;
- 动画结束后停止 indicator。
具体的代码可以参考上文代码块⬆️
取消正在进行的异步下载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
NSString *validOperationKey = context[SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey];
if (!validOperationKey) {
validOperationKey = NSStringFromClass([self class]);
SDWebImageMutableContext *mutableContext = [context mutableCopy];
mutableContext[SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey] = validOperationKey;
context = [mutableContext copy];
}
[self sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey:validOperationKey];
...
[self sd_setImageLoadOperation:operation forKey:validOperationKey];
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| - (void)sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
if (key) {
SDOperationsDictionary *operationDictionary = [self sd_operationDictionary];
id<SDWebImageOperation> operation;
@synchronized (self) {
operation = [operationDictionary objectForKey:key];
}
if (operation) {
if ([operation respondsToSelector:@selector(cancel)]) {
[operation cancel];
}
@synchronized (self) {
[operationDictionary removeObjectForKey:key];
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| - (void)sd_setImageLoadOperation:(nullable id<SDWebImageOperation>)operation forKey:(nullable NSString *)key {
if (key) {
if (operation) {
SDOperationsDictionary *operationDictionary = [self sd_operationDictionary];
@synchronized (self) {
[operationDictionary setObject:operation forKey:key];
}
}
}
}
|
这里引用学长的一段话:
实际上,所有的操作都是由一个实际上,所有的操作都是由一个operationDictionary字典维护的,执行新的操作之前,cancel所有的operation。
通俗来说:这两个方法的组合使用,可以实现对图片加载操作的管理。在设置新的图片加载操作之前,会先取消之前的操作,从而确保每个视图只执行最新的图片加载操作。 这样可以避免出现重复加载或并发加载的问题,同时也提高了图片加载的效率和用户体验。
- 重复加载: 指的是在同一时间点或短时间内多次加载相同资源的情况。这可能是由于代码逻辑错误、用户操作或系统问题导致的。重复加载可能会造成资源浪费、性能下降和不必要的网络请求。
- 并发加载: 指的是在同一时间点或短时间内同时进行多个加载操作的情况。这种情况通常发生在多线程或并发执行的环境下,多个加载操作可以同时进行,以提高效率和响应性。但是必须确保每个加载操作独立处理自己的资源,否则会出现数据竞争和冲突。
下载图片
这个操作是由一个SDWebImageManager完成的,是一个单例
1
2
3
4
5
| - (nullable SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)loadImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nonnull SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock;
|
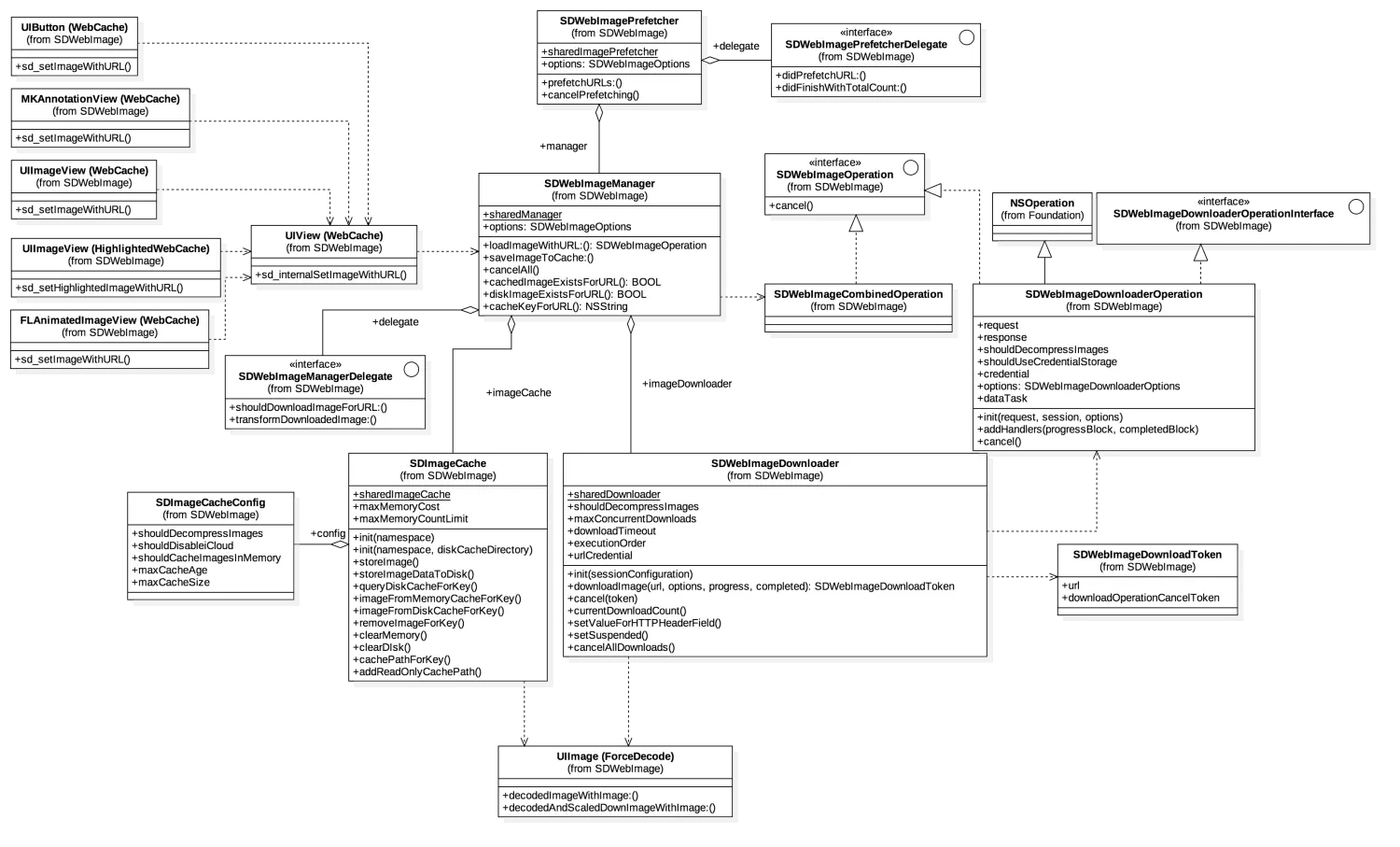
实际使用中并不直接使用SDWebImageDownloader和SDImageCache类对图片进行下载和存储,而是使用SDWebImageManager来管理。包括平常使用UIImageView+WebCache等控件的分类,都是使用SDWebImageManager来处理,该对象内部定义了一个图片下载器(SDWebImageDownloader)和图片缓存(SDImageCache)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @interface SDWebImageManager : NSObject
@property (weak, nonatomic) id <SDWebImageManagerDelegate> delegate;
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) SDImageCache *imageCache;
@property (strong, nonatomic, readonly) SDWebImageDownloader *imageDownloader;
...
@end
|
他的几个核心api:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithCache:(nonnull id<SDImageCache>)cache loader:(nonnull id<SDImageLoader>)loader NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
- (id )downloadImageWithURL:(NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
progress:(SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(SDWebImageCompletionWithFinishedBlock)completedBlock;
- (void)saveImageToCache:(UIImage *)image forURL:(NSURL *)url;
- (void)cancelAll;
- (BOOL)isRunning;
- (BOOL)cachedImageExistsForURL:(NSURL *)url;
- (BOOL)diskImageExistsForURL:(NSURL *)url;
- (void)cachedImageExistsForURL:(NSURL *)url
completion:(SDWebImageCheckCacheCompletionBlock)completionBlock;
- (void)diskImageExistsForURL:(NSURL *)url
completion:(SDWebImageCheckCacheCompletionBlock)completionBlock;
- (NSString *)cacheKeyForURL:(NSURL *)url;
|
下载图片的主要过程,也是这几个方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| - (nullable SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)loadImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nonnull SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock;
|
SDWebImageDownloader
具体的网络操作由SDWebImageDownloaderOperation对象处理,图片的下载是放在一个NSOperationQueue完成的
1
| @property (strong, nonatomic, nonnull) NSOperationQueue *downloadQueue;
|
默认情况的最大并发数是6,如果需要我们可以通过maxConcurrentDownloads修改
通过观察- (nullable SDWebImageDownloadToken *)downloadImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context progress:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock completed:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock的代码,我们可以看出来,SDWebImageDownloader把operation加到队列中执行:
1
2
|
[self.downloadQueue addOperation:operation];
|
这两行代码是SDWebImageDownloader开启下载任务的==关键==:
- 生成下载任务的Operation操作;
- 将Operation操作加入到队列中,实现异步任务下载;
SDWebImageOptions
参数列表中有一项SDWebImageOptions,这.h文件中定义了一个可以暴露在外的选择方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, SDWebImageOptions) {
SDWebImageRetryFailed = 1 << 0,
SDWebImageLowPriority = 1 << 1,
SDWebImageCacheMemoryOnly = 1 << 2,
SDWebImageProgressiveDownload = 1 << 3,
SDWebImageRefreshCached = 1 << 4,
SDWebImageContinueInBackground = 1 << 5,
SDWebImageHandleCookies = 1 << 6,
SDWebImageAllowInvalidSSLCertificates = 1 << 7,
SDWebImageHighPriority = 1 << 8,
SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder = 1 << 9,
SDWebImageTransformAnimatedImage = 1 << 10,
};
|
SDImageCache
SDWebImage.h这个类在源代码有这样一个注释,翻译过来大概就是
它维护了一个内存缓存和一个可选的磁盘缓存
磁盘缓存写入操作是异步执行的,因此不会给 UI 增加不必要的延迟。这个类还有个私有类SDMemoryCache,它继承自自NSCache,负责管理图像的内存缓存,其内部就是将NSCache 扩展为了SDMemoryCache 协议,并为iOS/tvOS平台添加了@property (nonatomic, strong, nonnull) NSMapTable<KeyType, ObjectType> *weakCache; // strong-weak cache,并为其添加了信号量锁来保证线程安全。
weakCache 的作用在于恢复缓存,它通过 CacheConfig 的 shouldUseWeakMemoryCache开关以控制。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| - (void)storeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image
imageData:(nullable NSData *)imageData
forKey:(nullable NSString *)key
toMemory:(BOOL)toMemory
toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk
completion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock;
|
该方法将图像异步缓存到指定密钥下的内存中,可以选择是否缓存到磁盘中,并且可以直接将图像的数据保存到磁盘中,就不必再通过将原图像编码后获取图像的数据再保存到磁盘中,以节省硬件资源.
刚才我们可能注意到,下载的方法中都有一个SDImageType的参数
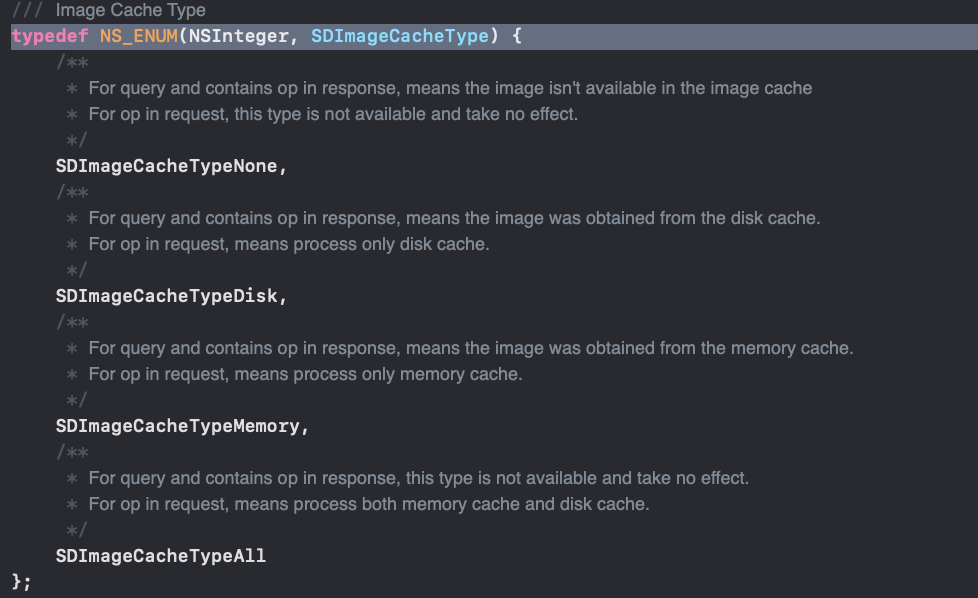
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, SDImageCacheType) {
SDImageCacheTypeNone,
SDImageCacheTypeDisk,
SDImageCacheTypeMemory
};
|
设置最大缓存和时间设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| SDImageCache类的源码
@property (assign, nonatomic) BOOL shouldDecompressImages;
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSUInteger maxMemoryCost;
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSInteger maxCacheAge;
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSUInteger maxCacheSize;
|
我们还可以设置maxCache
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| SDWebImageManager *manager = [SDWebImageManager sharedManager];
[manager.imageCache setMaxMemoryCost:1000000];
[manager.imageCache setMaxCacheSize:640000];
[manager.imageDownloader setMaxConcurrentDownloads:1];
[manager downloadImageWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://p9.qhimg.com/t01eb74a44c2eb43193.jpg"]
options:SDWebImageProgressiveDownload progress:^(NSInteger receivedSize, NSInteger expectedSize) {
NSLog(@"%lu", receivedSize);
} completed:^(UIImage *image, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL *imageURL) {
self.imageView1.image = image;
}];
[manager downloadImageWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://img.article.pchome.net/00/28/33/87/pic_lib/wm/kuanpin12.jpg"]
options:SDWebImageProgressiveDownload progress:^(NSInteger receivedSize, NSInteger expectedSize) {
NSLog(@"%lu", receivedSize);
} completed:^(UIImage *image, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL *imageURL) {
self.imageView2.image = image;
}];
NSUInteger size = [manager.imageCache getSize];
NSUInteger count = [manager.imageCache getDiskCount];
NSLog(@"size = %lu", size);
NSLog(@"count = %lu", count);
[manager.imageCache clearDisk];
size = [manager.imageCache getSize];
count = [manager.imageCache getDiskCount];
NSLog(@"sizeClean = %lu", size);
NSLog(@"countClean = %lu", count);
|
三种缓存(内存图片缓存、磁盘图片缓存、内存操作缓存)
- 先查看内存图片缓存,内存图片缓存没有,后生成操作,查看磁盘图片缓存
- 磁盘图片缓存有,就加载到内存缓存,没有就下载图片
- 在建立下载操作之前,判断下载操作是否存在
- 默认情况下,下载的图片数据会同时缓存到内存和磁盘中
1、内存缓存及磁盘缓存
内存缓存的处理由NSCache对象实现,NSCache类似一个集合的容器,它存储key-value对,类似于nsdictionary类,我们通常使用缓存来临时存储短时间使用但创建昂贵的对象,重用这些对象可以优化新能,同时这些对象对于程序来说不是紧要的,如果内存紧张就会自动释放。
磁盘缓存的处理使用NSFileManager对象实现,图片存储的位置位于cache文件夹,另外SDImageCache还定义了一个串行队列来异步存储图片。
SDImageCache提供了大量方法来缓存、获取、移除及清空图片。对于图片的索引,我们通过一个key来索引,在内存中,我们将其作为NSCache的key值,而在磁盘中,我们用这个key值作为图片的文件名,对于一个远程下载的图片其url实作为这个key的最佳选择。
2、存储图片
先在内存中放置一份缓存,如果需要缓存到磁盘,将磁盘缓存操作作为一个task放到串行队列中处理,会先检查图片格式是jpeg还是png,将其转换为响应的图片数据,最后吧数据写入磁盘中(文件名是对key值做MD5后的串)
3、查询图片
内存和磁盘查询图片API:
1
2
| - (UIImage *)imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:(NSString *)key;
- (UIImage *)imageFromDiskCacheForKey:(NSString *)key;
|
查看本地是否存在指定key的图片:
1
| - (NSOperation *)queryDiskCacheForKey:(NSString *)key done:(SDWebImageQueryCompletedBlock)doneBlock;
|
还有一些其他的常见接口和属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| (1)-getSize :获得硬盘缓存的大小
(2)-getDiskCount : 获得硬盘缓存的图片数量
(3)-clearMemory : 清理所有内存图片
(4)- removeImageForKey:(NSString *)key 系列的方法 : 从内存、硬盘按要求指定清除图片
(5)maxMemoryCost : 保存在存储器中像素的总和
(6)maxCacheSize : 最大缓存大小 以字节为单位。默认没有设置,也就是为0,而清理磁盘缓存的先决条件为self.maxCacheSize > 0,所以0表示无限制。
(7)maxCacheAge : 在内存缓存保留的最长时间以秒为单位计算,默认是一周
|
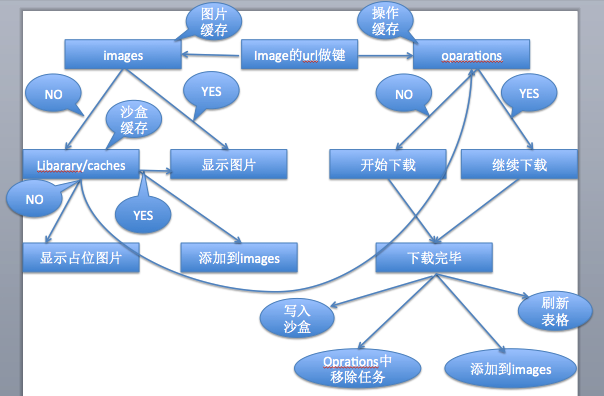
- SDWebImage的大部分工作是由缓存对象SDImageCache和异步下载器管理对象SDWebImageManager来完成的。
- SDWebImage的图片下载是由SDWebImageDownloader这个类来实现的,它是一个异步下载管理器,下载过程中增加了对图片加载做了优化的处理。而真正实现图片下载的是自定义的一个Operation操作,将该操作加入到下载管理器的操作队列downloadQueue中,Operation操作依赖系统提供的NSURLConnection类实现图片的下载。
三、小结
SDWebImage通过了一系列复杂的封装,把一个繁琐的过程封装成简单的接口来使用,实现了并发的图片下载及解压缩操作以及内存与磁盘存储等复杂功能